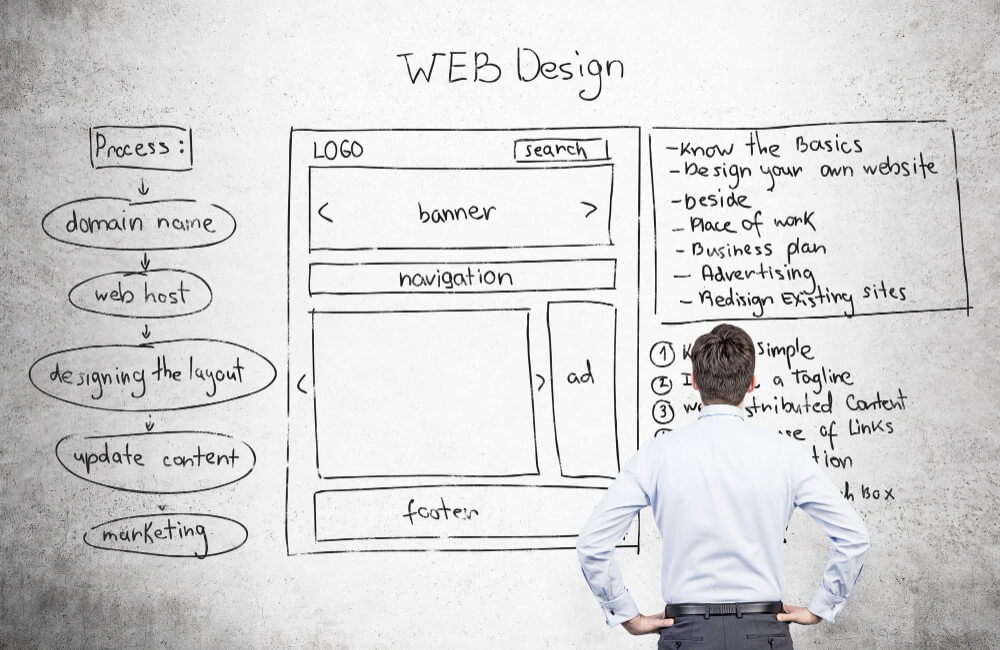
Brief background on importance of having a unique, branded website and how customizing an existing WordPress theme can help achieve that without needing full custom theme development.
Reasons to Customize Your Theme
- Reflect your brand visually
- Add/remove specific functionality
- Optimize site performance
- Make content easier to update
- Stand out from competition
Where to Start
- Choosing the right base theme
- Popular frameworks like Genesis or underscores
- Review theme features and flexibility
- Using child themes
- Avoid losing work from parent theme updates
- Overwrite parent CSS, templates, etc.
Customizing Design Elements
- Typography
- Font sizes, styles, line heights
- Heading and body fonts
- Colors
- Primary, secondary, accent colors
- Buttons, links, highlights
- Logos and graphics
- Favicon, header logo, other brand assets
Modifying Theme Structure and Layout
- Page templates
- Custom page layouts (e.g. homepage)
- Widget areas
- Sidebars, headers, footers
- Content elements
- Feature blocks, testimonials, etc.
Going Further: Code Modifications
- CSS customizations
- Advanced styling adjustments
- Template files
- Header, footer, archives, etc.
- Functions file
- Custom code snippets
Testing and Launching Your Customized Theme
- Preview on staging site
- Browser test for responsiveness
- Migrate live when ready
Includes practical examples of customizing popular Themeforest themes (e.g. Astra, GeneratePress) to achieve specific brand goals.